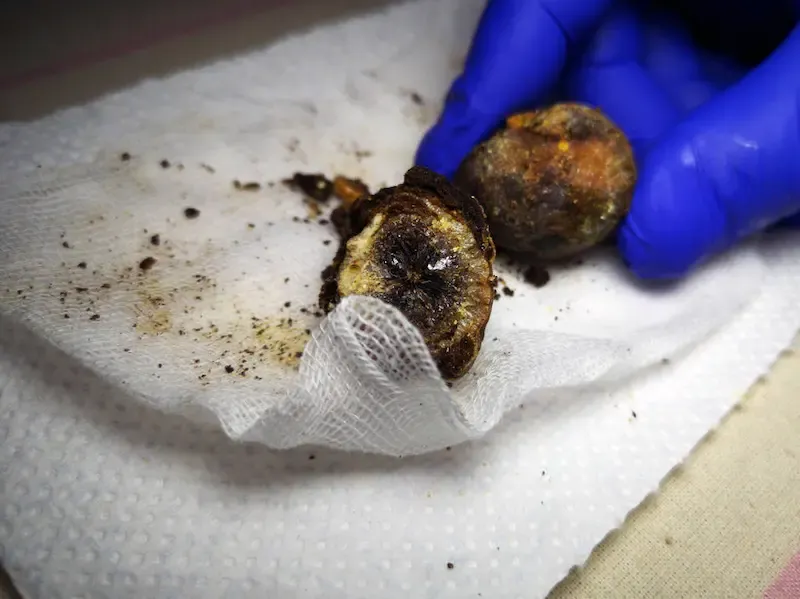
Gallstones, small hardened deposits in the gallbladder, silently affect the health of millions worldwide. These pebble-like formations can lead to severe discomfort and complications if left undetected. It is crucial to identify key symptoms early on to prevent further health issues. Gallbladder health is often overlooked until pain strikes suddenly, leaving many unaware of the underlying cause.
Recognizing these symptoms early can significantly impact one’s wellbeing. According to Dr. Susan Thomson, a gastroenterologist at Health First Clinic, “Early detection is vital because complications from untreated gallstones can escalate quickly.” Armed with this knowledge, individuals can take proactive steps to seek timely medical intervention and maintain their gallbladder health.
What Are Gallstones?
Gallstones are small, hardened deposits that form within the gallbladder, a small organ responsible for storing bile produced by the liver. They primarily occur when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile, such as cholesterol or bilirubin. There are two main types of gallstones: cholesterol and pigment stones. Cholesterol gallstones, which account for about 80% of cases in industrialized nations, are typically yellow-green and result from an excess of cholesterol in the bile. On the other hand, pigment stones are smaller, darker formations linked to elevated levels of bilirubin and often associated with conditions like liver cirrhosis or infections in the biliary tract.
The process by which these stones develop involves several factors. When bile contains excessive amounts of cholesterol, it can crystallize over time into solid particles. These particles may then clump together to form larger stones. In contrast, pigment stones emerge due to increased bilirubin production — often stemming from red blood cell breakdown — which can cause calcium compounds to precipitate out and solidify within the gallbladder. Understanding these mechanisms highlights why certain individuals might be more susceptible than others based on genetics, diet, or underlying health conditions.
Recognizing how gallstones form is crucial because their presence often goes unnoticed until they manifest symptoms such as abdominal pain. Pain usually occurs when a stone blocks one of the bile ducts leading from the gallbladder to the small intestine — a situation that can lead to intense sensations on your right side or between your shoulder blades upon consuming fatty foods. Therefore, distinguishing between cholesterol and pigment stones is not only essential for accurate diagnosis but also for devising proper treatment plans aimed at preventing recurrence and managing any potential complications effectively.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of gallstones early on can make a significant difference in managing the condition and preventing complications. Many individuals with gallstones may not experience any symptoms, leading to what’s known as “silent” gallstones. However, for those who do exhibit symptoms, these can often be mistaken for other digestive issues.
The most common signs of gallstones include abdominal pain, particularly after eating fatty meals, nausea, and changes in bowel movements. This pain typically occurs in the upper right portion of the abdomen and can last from a few minutes to several hours. It’s crucial to pay attention to this symptom’s severity and frequency since mild discomfort can escalate into more persistent or severe episodes over time.
In addition to abdominal pain, some sufferers might encounter back pain between their shoulder blades or right shoulder if the problem worsens. Symptoms like bloating, indigestion, and gas are also prevalent among gallstone patients and can sometimes be dismissed as ordinary digestive problems. Understanding these indicators’ severity is essential because they affect daily functioning and hint at potential biliary complications requiring medical evaluation. Recognizing them promptly helps ensure timely intervention by healthcare professionals.
Abdominal Pain: A Key Indicator
Abdominal pain stands out as a hallmark symptom for those suspecting gallstones. Unlike typical abdominal discomfort, pain associated with gallstones — often termed biliary colic — can be sudden and severe. This intense sharp or cramping sensation usually sets in after consuming a fatty meal, reflecting the body’s struggle to process fats when the bile flow is obstructed by stones. In addition to its abrupt onset, this pain can be unpredictable, rendering it crucial that individuals distinguish between ordinary digestive issues and possible gallstone trouble.
Gallstone-related pain is typically concentrated in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen; however, it might also radiate towards the back or right shoulder blade. This specific location aids healthcare professionals in differentiating between common stomach-aches and potential gallbladder issues. While common abdominal pain can subside within a few hours or respond well to over-the-counter medication, biliary colic often persists longer and demonstrates resistance to typical treatments. Patients should note both the intensity and duration of their discomfort as these are critical clues pointing toward gallstone complications.
Dr. Emily Stevens, a gastroenterologist at City Hospital, suggests that “within two to three hours post-meal is when patients start feeling this distinctive pain,” alerting them that something may be awry with their digestive system. Accompanying symptoms such as nausea further complicate one’s daily routine, underscoring the urgency of identifying whether unusual abdominal sensations signal an underlying issue like gallstones. Individuals who observe consistent patterns or experience progressive worsening of pain are advised to seek medical evaluation promptly.
Nausea and Vomiting: Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms that often accompany gallstone-related discomfort. While these symptoms can result from various conditions, their occurrence in combination with specific abdominal pain should not be dismissed lightly. Gallstones may cause nausea as the digestive process is disrupted, leading to a sensation of queasiness. When attempting to digest fatty meals, this nauseous feeling may intensify due to the gallstones obstructing bile flow, which plays a crucial role in breaking down fats.

Vomiting, although sometimes attributed to everyday illnesses like stomach bugs or food poisoning, becomes particularly concerning when it links with gallstones. Persistent vomiting can signify severe complications, such as an inflamed gallbladder or major obstruction in the bile duct, both requiring urgent medical evaluation. Health professionals stress that recurrent episodes of vomiting paired with known gallstone symptoms warrant immediate attention to rule out potential threats like pancreatitis or cholecystitis.
In such scenarios, ignoring these signs could lead to escalated health risks. Dr. Emily Jacobs, a gastroenterologist at Riverside Hospital, highlights: “Vomiting associated with gallstones isn’t simply inconvenient; it’s indicative of possible serious underlying issues.” By acknowledging this correlation early and seeking prompt healthcare guidance, individuals can prevent further complications and avoid potentially invasive treatments by addressing gallstone concerns proactively.
Changes in Bowel Movements
Gallstones can significantly impact digestion, leading to noticeable changes in bowel habits. When the gallbladder is obstructed by stones, bile drainage into the small intestine is disrupted. Bile plays a crucial role in breaking down fats during digestion; when its flow is impaired, it can result in issues that manifest as symptoms noticeable in your stool.
One symptom check for gallstone-related digestive disruption includes observing pale or clay-colored stools. This occurs because bilirubin — a component of bile responsible for giving stool its brown color — cannot reach the intestine due to blockage from gallstones. Additionally, you may notice that your stools are greasy or unusually foul-smelling. This reflects fat malabsorption caused by reduced bile availability, an essential element for emulsifying dietary fats.
It’s important not to overlook these persistent changes since they might hint at underlying gallstone problems. Dr. Emily Carter, a gastroenterologist at HealthPoint Medical Center, states, “Identifying these abnormal stool characteristics early is vital as they often precede more serious complications.” Paying attention to such signs can lead you to seek medical advice sooner and potentially avoid further health issues related to untreated gallstones.
Jaundice: A Serious Symptom
Jaundice is a notable warning that gallstones might have traveled beyond the gallbladder, potentially blocking the bile ducts. This obstruction prevents bilirubin — a yellow compound naturally released by the liver — from exiting the body, leading to a distinctive yellowing of the skin and eyes. While jaundice can result from various medical conditions, when linked to gallstones, it signifies a significant escalation in severity due to possible infection or liver damage.
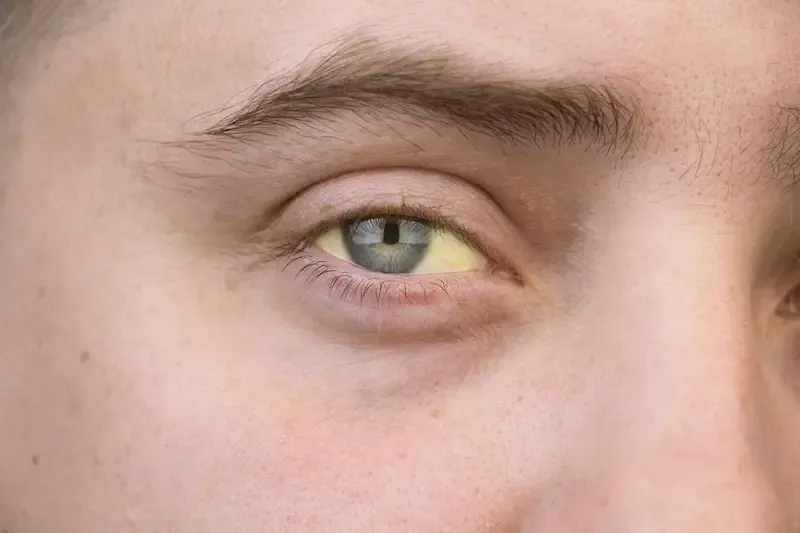

It is crucial for individuals experiencing jaundice to seek immediate medical attention, as this symptom can indicate serious complications. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a gastroenterologist at Riverside Medical Center, “The appearance of jaundice together with right upper abdominal pain often points towards an acute situation requiring urgent investigation.” Ignoring these signs may increase health risks such as pancreatitis or cholecystitis, which demand timely intervention.
Risk factors like obesity and rapid weight loss further exacerbate the likelihood of developing symptomatic gallstone disease. As highlighted by multiple studies, those with higher body mass indices tend to produce more cholesterol — which in turn increases their chances of forming stones that could cause blockages. Recognizing jaundice alongside other symptoms like unexplained fevers or chilling shivers underlines the necessity for prompt evaluation by healthcare professionals. Addressing these indicators swiftly reduces complication risks and ensures better health outcomes.
Fever and Chills: When Infection is a Risk
When gallstones become problematic, they can cause a fever accompanied by chills, indicative of a possible infection. This occurs when gallstones block the bile ducts, leading to inflammation or infections such as cholangitis or cholecystitis. According to Dr. Emily Tran, a specialist in gastrointestinal health, “A sudden spike in temperature along with other symptoms should raise immediate concern.” Such fevers often present alongside abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting — symptoms that collectively warrant urgent medical evaluation.
Untreated gallstones risk leading to severe complications like infections that can spread beyond the gallbladder. Inflammation caused by these stones often results in pus formation within the bile duct system. This situation not only exacerbates abdominal discomfort but also increases the likelihood of sepsis, which is life-threatening if it progresses unchecked. It’s vital for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek immediate attention; healthcare providers may use ultrasound diagnosis to confirm the presence of gallstones.
An ultrasound diagnosis is central not just in identifying gallstones but also in assessing any related infections by visualizing possible ductal obstructions. Early detection plays a crucial role in preventing further complications including liver damage due to prolonged obstruction and infection spread. Timely intervention with antibiotics or even surgical procedures might be required depending on the severity of the condition, emphasizing why proactive healthcare management is essential in handling such risks associated with gallstones effectively.
Diagnosis: Seeking Professional Help
Diagnosing gallstones accurately requires the expertise of healthcare professionals and a series of tests. One prevalent method is an ultrasound scan, which provides images of the gallbladder to detect any stones present. Another diagnostic tool often used is an endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), especially when stones might be lodged in bile ducts. In some instances, doctors might recommend a CT scan or MRI to provide detailed images for further evaluation.
Consulting a healthcare professional for these diagnostic tests is crucial. Gallstone symptoms can resemble other conditions such as pancreatitis or peptic ulcers, making self-diagnosis unreliable and potentially dangerous. Doctors not only confirm the presence of gallstones but also ascertain their type and size, which significantly impacts potential treatment options. Cholesterol stones form differently than pigment stones, requiring distinct approaches to manage effectively.
Early consultation with medical experts offers numerous benefits beyond diagnosis alone. Professionals provide guidance on various treatment options — ranging from lifestyle changes and medications like bile acids that dissolve cholesterol stones to surgical procedures such as cholecystectomy for severe cases. Timely intervention helps prevent complications like gallbladder inflammation or infections linked to untreated gallstones, ensuring better health outcomes for patients.
In seeking out professional evaluation and advice, individuals safeguard their health journey against improper treatments based on guesswork. A structured approach towards diagnosing and treating gallstones is fundamental in addressing symptoms efficiently while preventing future risks associated with this common yet serious medical condition.
Being Vigilant About Gallstones
Understanding the symptoms and risks associated with gallstones is crucial for maintaining good health. Key signs such as persistent abdominal pain, nausea, changes in bowel movements, jaundice, fever, and chills are vital indicators of potential gallstone issues. Recognizing these symptoms early can prevent complications that often require medical intervention. Healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of not ignoring these warning signals and seeking diagnosis through appropriate tests to confirm their presence.
Proactive management of your health is essential when dealing with potential gallstone concerns. The ability to identify notable symptoms at an early stage allows individuals to seek timely professional advice and initiate necessary treatment paths. Encouraging a proactive approach to health could mitigate the risks associated with untreated gallstones, which can lead to severe consequences like infections or bile duct obstructions. By staying informed and taking swift action, individuals can better manage their well-being and reduce the likelihood of future complications related to gallstones.





