The Long-Term Effects of Poor Ergonomics
Poor ergonomics in the workplace can have significant long-term effects on your health. One of the most common consequences is the development of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). These disorders can affect your muscles, tendons, ligaments, joints, and other soft tissues, causing symptoms such as pain, stiffness, weakness, and reduced flexibility.
Office environments, in particular, pose unique challenges for maintaining good ergonomics. Prolonged use of computers and other digital devices can strain our eyes, leading to eye strain and even more serious vision problems. It is important to position your computer monitor at eye level, ensuring that your head is aligned with your spine. Additionally, taking regular breaks to rest your eyes can help mitigate eye strain.
Taking action now to address poor ergonomics in your workplace is crucial. Implementing ergonomic interventions such as providing ergonomic equipment, conducting risk assessments, and offering ergonomic training can help reduce the risk of MSDs and associated symptoms.
By promoting neutral postures, encouraging regular breaks, and ensuring proper equipment set up, you can help prevent long-term health issues and potential compensation claims.
Musculoskeletal Disorders
Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) are a prevalent issue in today’s modern workforce, affecting individuals across various industries. These disorders, which primarily involve the muscles, bones, tendons, and ligaments, can cause significant pain, discomfort, and limitations in daily activities.
Poor ergonomics, such as improper posture, repetitive movements, and prolonged static positions, are major contributors to the development of MSDs. Office workers, in particular, are at a high risk of developing MSDs due to the nature of their work, which often involves long hours of sitting at a desk and using computers.
It is crucial to address these risks and take proactive measures to prevent the onset of MSDs, as they can have long-term effects on an individual’s overall health and quality of life.
Types of Musculoskeletal Disorders
Musculoskeletal disorders are a common consequence of poor ergonomics in the workplace. These disorders refer to a wide range of conditions that affect the soft tissues in the body, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels.
Muscle Strain
One type of musculoskeletal disorder is muscle strain, which occurs when the muscles are overworked or subjected to repetitive movements. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Tendonitis
Tendonitis is another disorder that affects the tendons, causing inflammation and pain. Ligament sprains can occur when the ligaments are stretched or torn, resulting in pain and instability of the affected joint.

Repetitive Strain Injury
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is a common musculoskeletal disorder that affects the nerves in the hands, wrists, and arms. It is caused by repetitive movements or overuse of these body parts, leading to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling.
Varicose
Poor ergonomics can also have a negative impact on the blood vessels, increasing the risk of varicose veins. Varicose veins occur when the blood vessels become swollen and twisted, causing discomfort and aching in the affected areas.
It is important to address poor ergonomics to prevent these types of musculoskeletal disorders. Implementing proper ergonomic practices, such as maintaining neutral postures, using ergonomic equipment, and taking regular breaks, can help reduce the risk of soft tissue injuries and promote overall musculoskeletal health.
Risk Factors for Developing Musculoskeletal Disorders
There are several risk factors associated with the development of musculoskeletal disorders. Poor posture, repetitive movements, improper workstation set up, and prolonged periods of sitting are some of the main contributors to these disorders.
Poor Posture
Poor posture, such as slouching or hunching over, can put excessive strain on the muscles, ligaments, and tendons. This can lead to muscle imbalances, fatigue, and increased risk of injury in the long run.
Repetitive Movements
Repetitive movements, such as typing or using a mouse for extended periods of time, can cause overuse injuries like tendonitis and RSI. These repetitive actions put a constant strain on the muscles and tendons involved, leading to inflammation and pain.
Improper Workstation Set up
Improper workstation set up is another significant risk factor. If your workstation is not ergonomically designed, it can force you into awkward postures and repetitive movements. This can put excessive strain on your musculoskeletal system, leading to discomfort and increased risk of injury.
Prolonged Periods of Sitting
Prolonged periods of sitting can also contribute to the development of musculoskeletal disorders. Sitting for extended periods without taking breaks to stretch or move around can cause muscle imbalances, reduced blood flow, and increased pressure on the spine and joints.

Inadequate Rest Breaks
Other relevant risk factors include inadequate rest breaks, which can lead to overexertion and fatigue, and high levels of stress, which can result in muscle tension and increased susceptibility to musculoskeletal pain.
In order to reduce the risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders, it is important to address these risk factors. Implementing ergonomic workstation set ups, practicing proper posture, taking regular breaks to stretch and move, and managing stress levels can all contribute to maintaining musculoskeletal health.
Common Symptoms Associated with Musculoskeletal Disorders
Musculoskeletal disorders can cause a range of symptoms that can significantly impact daily activities and overall well-being. Common symptoms include pain, tingling, swelling, loss of muscle function, and discomfort.
Sharp and Dull Pain
Pain is one of the most prevalent symptoms associated with musculoskeletal disorders. It can be dull or sharp and can occur in specific areas or spread throughout the body. The pain can range from mild to severe, making it difficult to perform regular tasks and activities.
Tingling Sensations
Tingling sensations, also known as paresthesia, are another common symptom. This sensation can feel like pins and needles or a burning sensation. It can occur in the affected muscles or radiate down the arms or legs.
Swelling or Edema
Swelling, or edema, may also be present in musculoskeletal disorders. Swelling occurs due to inflammation and fluid accumulation in the affected area. This can lead to discomfort, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
Loss of Muscle Function
Loss of muscle function is another symptom that can significantly impact everyday life. It can result in weakness, difficulty gripping or lifting objects, and challenges with coordination and balance.
Discomfort
Discomfort is a general term that encompasses various sensations like stiffness, soreness, or aching. It can be constant or intermittent and can worsen with movement or specific activities.
These symptoms can limit a person’s ability to perform routine tasks, participate in physical activities, and negatively affect their overall quality of life. Seeking medical attention and implementing appropriate treatment and management strategies is crucial to alleviate these symptoms and prevent further complications.
Poor Posture & Eye Strain
Poor posture and eye strain are two common problems associated with poor ergonomics in office environments. Sitting for extended periods of time in awkward postures can lead to musculoskeletal symptoms such as muscle strain, neck and back pain, and upper limb disorders.
Effects of Poor Posture on the Body
Poor posture can have a significant impact on the body, leading to discomfort, aches, and pain. When our posture is not aligned properly, it puts stress on our joints and ligaments, leading to malalignment. This malalignment can cause discomfort and pain in various areas of the body, including the neck, shoulders, back, and hips.

Negatively Affects the Muscles
In addition to joint and ligament discomfort, poor posture can also negatively affect the muscles. When we maintain a slouched or hunched position for extended periods of time, it can restrict blood circulation to the muscles. This lack of circulation can result in discomfort and decreased muscle performance. Muscles that receive inadequate blood flow may feel tight, stiff, and fatigued.
Causes Nerve Damage
Furthermore, poor posture can also cause nerve damage, leading to additional symptoms such as tingling, numbness, and pain. When our posture is not aligned correctly, it can put pressure on the nerves in certain areas of the body, causing nerve impingement. This impingement can result in tingling sensations, numbness, and even shooting pains.
Take Proper Action
Taking action to improve posture is crucial in preventing these negative effects on the body. Maintaining proper alignment and practicing good ergonomics can help alleviate discomfort, promote better circulation to the muscles, and reduce the risk of nerve damage. Investing in ergonomic equipment, such as an ergonomic chair and desk, can provide support and help maintain a neutral posture. Regular breaks and stretches throughout the day can also help alleviate muscle tension and promote blood flow.
Effects of Eye Strain on Vision and Health
Eye strain is a common issue that can significantly impact vision and overall health. When the muscles of the eyes are overworked due to extended periods of screen time or focusing on near objects, it can lead to eye muscle fatigue. This fatigue can cause symptoms such as blurry vision, difficulty focusing, and eye discomfort.
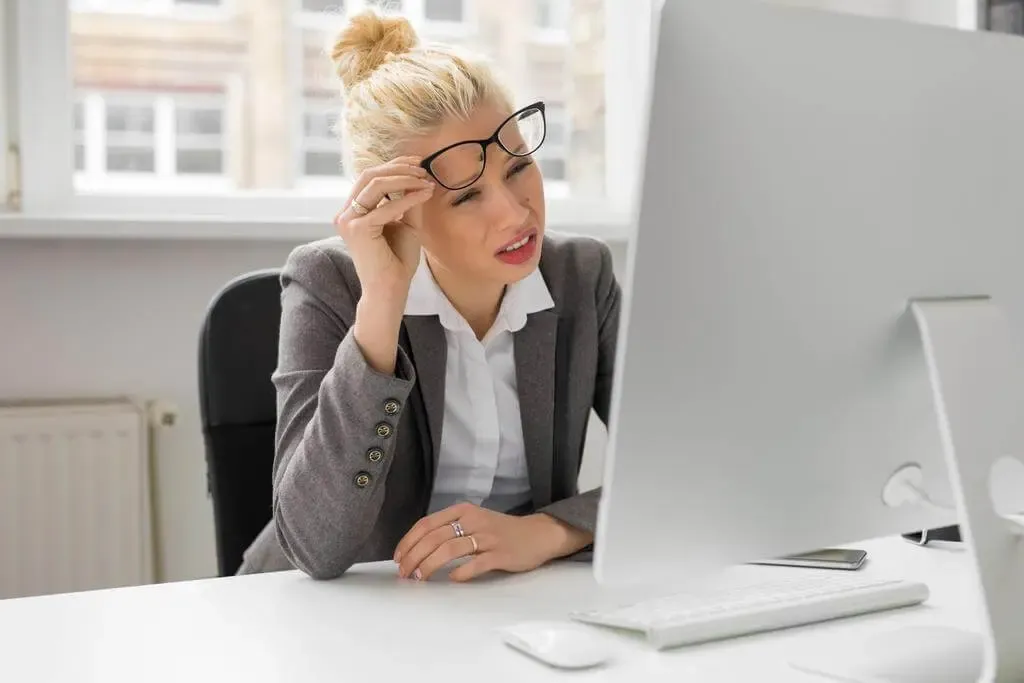

Glare from Screens and Improper Monitor Positioning
Glare from screens or improper monitor positioning can also contribute to eye strain. Bright lights or reflections on the screen can make it harder for the eyes to focus, leading to increased strain. It is important to position the monitor at eye level and use screen filters to reduce glare and minimize eye strain.
Lack of Blinking
Another factor that can contribute to eye strain is the lack of blinking. When we are engaged in tasks that require intense visual concentration, such as reading or working on a computer, we tend to blink less frequently. This reduces the moisture on the surface of the eyes, leading to dryness and irritation.
Take Preventative Measures
Preventative measures can be taken to alleviate eye strain and promote better eye health. Repositioning the monitor to reduce glare, using screen filters to minimize eye strain, and maintaining a well-lit environment can help prevent eye strain. It is also important to remember to blink regularly, especially during prolonged periods of visual concentration.
Protecting our eyes from eye strain is crucial for maintaining good vision and overall health. By implementing these preventive measures, we can reduce the risk of eye muscle fatigue, blurry vision, and discomfort, allowing us to continue working and enjoying screen time with greater ease and comfort.
How to Avoid Poor Posture & Eye Strain in Office Environments
Office environments can pose significant risks to our posture and eye health if proper ergonomics are not followed. Here are some steps and tips to help you avoid poor posture and eye strain while working:
1. Set up an ergonomic workstation: Ensure your desk, chair, and computer monitor are properly aligned. For proper ergonomics, it is recommended to have a chair that offers lumbar support and to have your feet flat on the floor or on a footrest. The top of your computer monitor should be at eye level.
2. Take regular breaks: It is recommended to take regular breaks and avoid sitting for extended periods of time. Stand up, stretch, and move around every 30-60 minutes. This helps relieve muscular fatigue and reduces the risk of musculoskeletal problems.
3. Maintain good posture: Sit up straight with your back supported against the chair. Maintain relaxed shoulders and avoid slouching or hunching forward. Place your keyboard and mouse within easy reach to avoid unnecessary strain.
4. Use proper lighting: Ensure your workspace is well-lit, but avoid glare or harsh lighting that can strain your eyes. Adjust curtains or blinds to minimize outside glare, and use task lighting to illuminate your work area.
5. Practice the 20-20-20 rule: Every 20 minutes, look away from your screen and focus on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. This reduces eye strain and helps maintain healthy eye moisture.
Maintaining good posture and preventing eye strain in the office is crucial for both employers and employees. It reduces muscular fatigue, discomfort, and the risk of musculoskeletal problems, leading to improved productivity, reduced sick leave, and lower healthcare costs.
Moreover, poor posture can negatively affect relationships, as it may project a lack of confidence and professionalism. It can also decrease overall well-being by causing muscle imbalances, decreased energy levels, and increased stress. By implementing proper office ergonomics and making these small changes, we can create a healthier and more productive work environment for all.
Ergonomic Workstation Set Up Tips
Having a properly set up ergonomic workstation is crucial for maintaining good health and preventing long-term negative effects on your body. Poor ergonomics can lead to a range of musculoskeletal disorders and other health issues.
To avoid these problems, follow these ergonomic workstation set up tips:
Adjusting Your Chair Height and Angle
Properly Adjust the Height and Angle of Your Chair
To create a comfortable and ergonomic workstation, it is essential to properly adjust the height and angle of your chair. By taking the time to set up your chair correctly, you can minimize the risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders and promote a healthier posture.
Start by ensuring that your feet are resting firmly on the ground and that your thighs are parallel to the floor. This can be achieved by adjusting the height of your chair. If you find that your feet are not flat on the ground, consider using a footrest to achieve the correct height.
Adjust the Backrest of Your Chair to Support Your Lower Back
Next, adjust the backrest of your chair to support your lower back. This will help maintain the natural curve of your spine and reduce strain on your back muscles. Make sure your chair allows for easy swiveling and rolling, enabling you to move freely without having to strain or twist your body.

By making these adjustments, you can create a more ergonomic workstation that promotes neutral postures and reduces the risk of musculoskeletal pain or discomfort. Taking the time to set up your chair correctly will go a long way in preventing long-term health issues associated with poor ergonomics.
Remember, investing in an ergonomic chair and other ergonomic equipment can further enhance your workstation set up, ensuring optimal comfort and minimizing the risk of injury. Prioritizing your ergonomics now can lead to long-term benefits for your overall health and well-being.
Working at Eye Level
Working at eye level is crucial for maintaining proper ergonomics in the office. When your monitor is positioned correctly, it reduces eye strain and improves overall comfort, leading to increased productivity and reduced risk of eye-related issues.
Position Your Monitor at the Correct Distance and Height
Positioning the monitor at the correct distance and height is key. The top of the screen should be at or slightly below eye level. This ensures that your neck is in a neutral position, reducing strain on the muscles and preventing discomfort. Moreover, it helps maintain proper posture by keeping your head and spine aligned.
To achieve the optimal eye level, there are practical tips you can follow. Consider using a monitor stand or adjustable arm to bring the screen to the desired height. If this is not available, adjust the height of your chair so that your eyes align with the top of the monitor.

Additionally, make sure the monitor is at the right distance from your eyes. Position it about an arm’s length away, maintaining a comfortable viewing distance.
By working at eye level, you can significantly reduce eye strain and improve your overall comfort while working. Implementing these simple adjustments is essential for maintaining good posture, preventing musculoskeletal pain, and promoting long-term health in the office.
Adopting Neutral Postures for the Upper Limbs
Adopting neutral postures for the upper limbs is crucial for maintaining good posture and preventing musculoskeletal disorders. When the upper limbs are held in neutral, relaxed positions, it reduces strain on the muscles, tendons, and joints, reducing the risk of injury and discomfort.
Imbalance of opposing forces and muscle activity can lead to poor alignment and potential injury. When certain muscles are constantly engaged or overused, while others are underused or weak, it creates an imbalance. This imbalance can disrupt the natural alignment of the upper limbs and affect the overall posture of the body.
The sedentary nature of many jobs, combined with a lack of exercise, can contribute to muscle imbalance. Spending extended periods of time in incorrect alignment, such as slouching or leaning forward, further exacerbates the problem.
Focus on Joint Alignment
To achieve neutral postures for the upper limbs, it is important to focus on joint alignment. Proper alignment of the shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints ensures that the muscles and tendons are working in harmony, supporting the body’s natural posture.
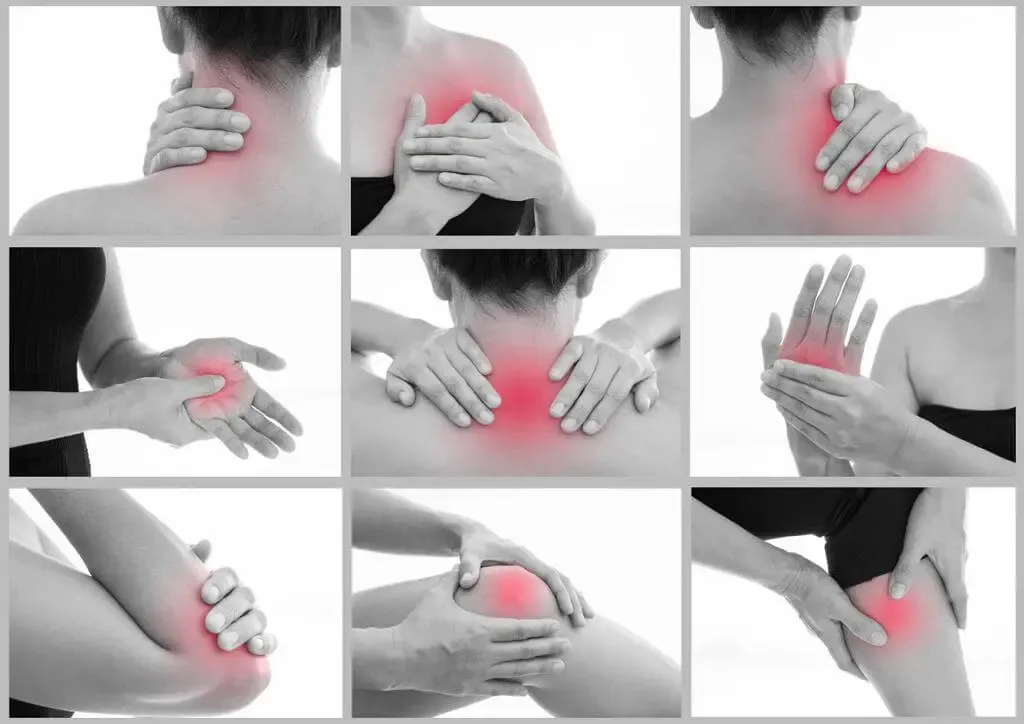
By actively adopting neutral postures for the upper limbs and addressing factors that contribute to muscle imbalance, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders. Regular exercise, ergonomic interventions, and maintaining awareness of posture and alignment can all play a crucial role in preventing discomfort and promoting long-term musculoskeletal health.
Conclusion
Ergonomics is essential for maintaining comfort, preventing injury, and promoting long-term health in the office. Investing in ergonomic equipment to create a comfortable workstation set up is an investment that can benefit your overall well-being. Working at eye level and adopting neutral postures for the upper limbs are key aspects of achieving good posture and reducing muscle strain.
Furthermore, by working together, employers and employees can significantly reduce the risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders. By implementing these simple adjustments, everyone can enjoy improved posture and reduced fatigue in the workplace.





