Introduction
Glioblastoma is a highly aggressive form of brain cancer that affects thousands of people around the world. This devastating disease requires urgent attention and understanding due to its complex nature and limited treatment options. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of glioblastoma, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the latest advancements in research. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of this formidable disease and its impact on individuals and their loved ones.
1. Understanding Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, also known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is a malignant brain tumor that arises from the glial cells in the brain. Glial cells provide support and nourishment to the neurons and play a crucial role in brain function. Glioblastoma is classified as a grade IV tumor, indicating its high aggressiveness and rapid growth.
2. Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of glioblastoma remains unknown. However, several risk factors have been identified, including genetic predisposition, exposure to ionizing radiation, and certain hereditary conditions such as neurofibromatosis and Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Additionally, older age and a history of previous brain tumors may increase the risk of developing glioblastoma.
3. Recognizing the Symptoms
Glioblastoma can manifest through various symptoms, which may vary depending on the tumor’s location within the brain. Common symptoms include persistent headaches, seizures, cognitive decline, personality or behavioral changes, visual disturbances, and motor skill impairments. It is essential to seek medical attention promptly if these symptoms arise.
4. Diagnosing Glioblastoma
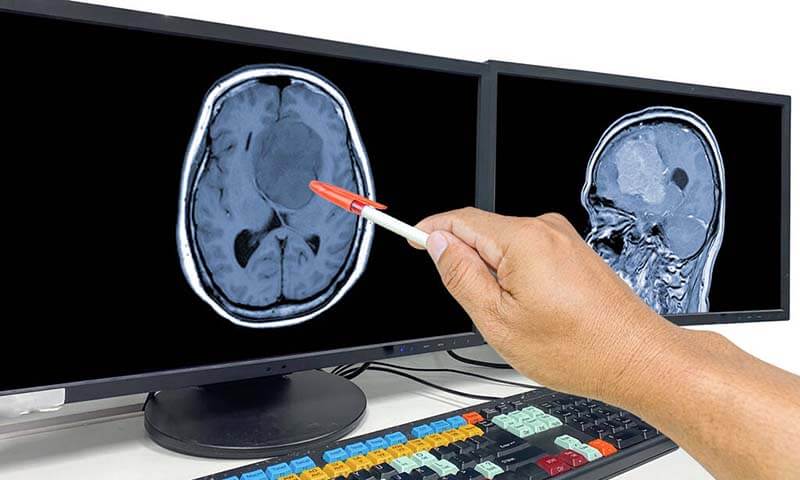
To diagnose glioblastoma, a series of tests and procedures are conducted. These may include neurological examinations, imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, and a biopsy to analyze the tumor tissue. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment strategy.
5. Treatment Approaches
Treating glioblastoma requires a multidisciplinary approach involving various treatment modalities. The primary treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Depending on the patient’s condition and tumor characteristics, these treatments may be used individually or in combination.
6. Surgery for Glioblastoma
Surgery plays a critical role in the management of glioblastoma. The primary goal of surgery is to remove as much of the tumor as possible while preserving brain function. However, complete removal is often challenging due to the infiltrative nature of glioblastoma cells.
7. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is commonly used in combination with surgery to target any remaining tumor cells. It involves the use of high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells and inhibit their ability to multiply. Advanced techniques such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and proton therapy help minimize damage to healthy brain tissue.
8. Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Chemotherapy drugs are administered to target and kill glioblastoma cells throughout the body. However, due to the blood-brain barrier, which limits the passage of substances into the brain, traditional chemotherapy is less effective against glioblastoma. Targeted therapy, on the other hand, focuses on specific molecular alterations within the tumor cells to inhibit their growth and division.
9. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy has emerged as a promising treatment approach for glioblastoma. It utilizes the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, therapeutic vaccines, and adoptive cell transfer are among the immunotherapeutic strategies being explored for glioblastoma treatment.
10. Emerging Treatment Options
Researchers and scientists are continuously striving to develop innovative treatment options for glioblastoma. These include novel drug therapies, gene therapy, oncolytic virus therapy, and nanotechnology-based approaches. While these advancements are still in the experimental stage, they hold great potential for improving patient outcomes in the future.
11. Clinical Trials and Research
Participation in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to the advancement of glioblastoma research. Clinical trials aim to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new treatment methods, including targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and combination therapies. It is essential for patients to discuss clinical trial opportunities with their healthcare providers.
12. Coping with Glioblastoma
A glioblastoma diagnosis can be overwhelming for both patients and their families. It is crucial to establish a strong support system and seek emotional and practical assistance. Support groups, counseling services, and online resources can provide valuable support and guidance throughout the treatment journey.
13. Supportive Care and Palliative Measures
Supportive care focuses on managing the symptoms and side effects of glioblastoma treatment to improve the patient’s quality of life. Palliative care, which is often provided in conjunction with active treatment, aims to address physical, emotional, and spiritual needs. It is designed to enhance comfort and alleviate suffering.
14. Promising Advances in Glioblastoma Research
The field of glioblastoma research is dynamic and constantly evolving. Scientists are exploring various avenues to improve treatment outcomes, including targeted therapies, personalized medicine, immunotherapies, and innovative drug delivery systems. These advancements offer hope for the future and the possibility of better treatment options for glioblastoma patients.
Conclusion
Glioblastoma remains one of the most aggressive forms of brain cancer, posing significant challenges in terms of diagnosis and treatment. However, advancements in medical research and technology are gradually unraveling the complexities of this disease. Through a multidisciplinary approach, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, there is hope for improved outcomes and extended survival for glioblastoma patients.
FAQs
1. Is glioblastoma curable?
Glioblastoma is currently considered incurable. However, ongoing research and clinical trials offer hope for improved treatment options and extended survival rates.
2. How long can someone live with glioblastoma?
The prognosis for glioblastoma varies depending on several factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, tumor size, and response to treatment. On average, survival ranges from 12 to 15 months following diagnosis.
3. Are there any alternative therapies for glioblastoma?
While alternative therapies may provide symptomatic relief or support overall well-being, they should not be used as a substitute for conventional glioblastoma treatments. It is important to discuss any alternative therapy plans with your healthcare provider.
4. Can dietary and lifestyle practices help?
Making healthy lifestyle choices is an important part of managing glioblastoma. Eating a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular exercise may help to reduce fatigue and improve overall quality of life. Additionally, incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and meditation can help to manage symptoms and promote emotional well-being.